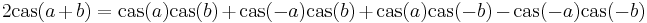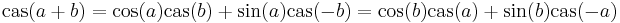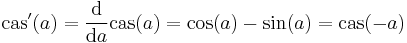Hartley transform
In mathematics, the Hartley transform is an integral transform closely related to the Fourier transform, but which transforms real-valued functions to real-valued functions. It was proposed as an alternative to the Fourier transform by R. V. L. Hartley in 1942, and is one of many known Fourier-related transforms. Compared to the Fourier transform, the Hartley transform has the advantages of transforming real functions to real functions (as opposed to requiring complex numbers) and of being its own inverse.
The discrete version of the transform, the Discrete Hartley transform, was introduced by R. N. Bracewell in 1983.
The two-dimensional Hartley transform can be computed by an analog optical process similar to an optical Fourier transform, with the proposed advantage that only its amplitude and sign need to be determined rather than its complex phase (Villasenor, 1994). However, optical Hartley transforms do not seem to have seen widespread use.
Contents |
Definition
The Hartley transform of a function f(t) is defined by:
where  can in applications be an angular frequency and
can in applications be an angular frequency and
is the cosine-and-sine or Hartley kernel. In engineering terms, this transform takes a signal (function) from the time-domain to the Hartley spectral domain (frequency domain).
Inverse transform
The Hartley transform has the convenient property of being its own inverse (an involution):
Conventions
The above is in accord with Hartley's original definition, but (as with the Fourier transform) various minor details are matters of convention and can be changed without altering the essential properties:
- Instead of using the same transform for forward and inverse, one can remove the
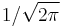 from the forward transform and use
from the forward transform and use 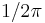 for the inverse—or, indeed, any pair of normalizations whose product is
for the inverse—or, indeed, any pair of normalizations whose product is 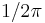 . (Such asymmetrical normalizations are sometimes found in both purely mathematical and engineering contexts.)
. (Such asymmetrical normalizations are sometimes found in both purely mathematical and engineering contexts.) - One can also use
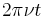 instead of
instead of 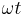 (i.e., frequency instead of angular frequency), in which case the
(i.e., frequency instead of angular frequency), in which case the 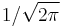 coefficient is omitted entirely.
coefficient is omitted entirely. - One can use cos−sin instead of cos+sin as the kernel.
Relation to Fourier transform
This transform differs from the classic Fourier transform 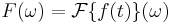 in the choice of the kernel. In the Fourier transform, we have the exponential kernel:
in the choice of the kernel. In the Fourier transform, we have the exponential kernel: 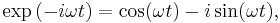 where i is the imaginary unit.
where i is the imaginary unit.
The two transforms are closely related, however, and the Fourier transform (assuming it uses the same 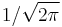 normalization convention) can be computed from the Hartley transform via:
normalization convention) can be computed from the Hartley transform via:
That is, the real and imaginary parts of the Fourier transform are simply given by the even and odd parts of the Hartley transform, respectively.
Conversely, for real-valued functions f(t), the Hartley transform is given from the Fourier transform's real and imaginary parts:
where 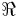 and
and 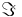 denote the real and imaginary parts of the complex Fourier transform.
denote the real and imaginary parts of the complex Fourier transform.
Properties
The Hartley transform is a real linear operator, and is symmetric (and Hermitian). From the symmetric and self-inverse properties, it follows that the transform is a unitary operator (indeed, orthogonal).
There is also an analogue of the convolution theorem for the Hartley transform. If two functions 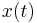 and
and 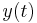 have Hartley transforms
have Hartley transforms 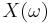 and
and 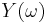 , respectively, then their convolution
, respectively, then their convolution 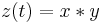 has the Hartley transform:
has the Hartley transform:
Similar to the Fourier transform, the Hartley transform of an even/odd function is even/odd, respectively.
cas
The properties of the cas function follow directly from trigonometry, and its definition as a phase-shifted trigonometric function 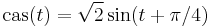 . For example, it has an angle-addition identity of:
. For example, it has an angle-addition identity of:
Additionally:
and its derivative is given by:
References
- Hartley, R. V. L., A more symmetrical Fourier analysis applied to transmission problems, Proc. IRE 30, 144–150 (1942).
- Bracewell, R. N., The Fourier Transform and Its Applications (McGraw-Hill, 1965, 2nd ed. 1978, revised 1986) (also translated into Japanese and Polish)
- Bracewell, R. N., The Hartley Transform (Oxford University Press, 1986) (also translated into German and Russian)
- Bracewell, R. N., Aspects of the Hartley transform, Proc. IEEE 82 (3), 381-387 (1994).
- Millane, R. P., Analytic properties of the Hartley transform, Proc. IEEE 82 (3), 413-428 (1994).
- Villasenor, John D., Optical Hartley transforms, Proc. IEEE 82 (3), 391-399 (1994).
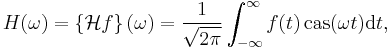
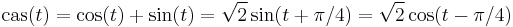
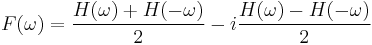
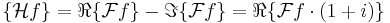
![Z(\omega) = \{ \mathcal{H} (x * y) \} = \sqrt{2\pi} \left( X(\omega) \left[ Y(\omega) %2B Y(-\omega) \right]
%2B X(-\omega) \left[ Y(\omega) - Y(-\omega) \right] \right) / 2](/2012-wikipedia_en_all_nopic_01_2012/I/cba05421b58ca5d530e0f0c94ecd0904.png)